Ademetionine
Ademetionine is a small molecule pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
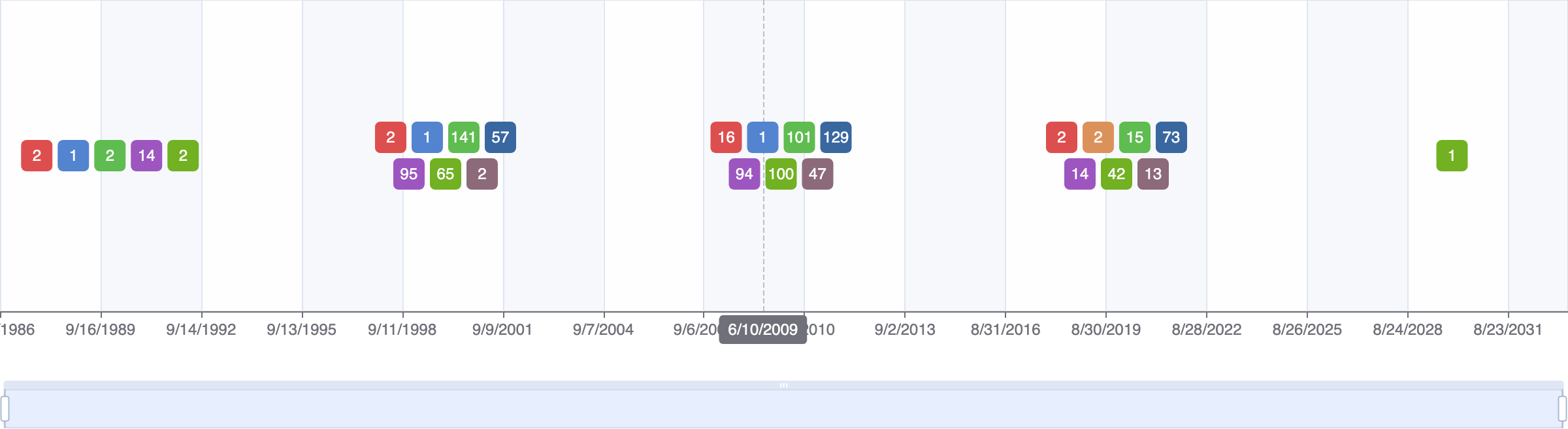
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
Therapeutic Areas
No data
Trade Name
FDA
EMA
No data
Drug Products
FDA
EMA
New Drug Application (NDA)
New Drug Application (NDA)
Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA)
Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA)
No data
Labels
FDA
EMA
No data
Indications
FDA
EMA
No data
Agency Specific
FDA
EMA
No data
Patent Expiration
No data
HCPCS
No data
Clinical
Clinical Trials
70 clinical trials
View more details
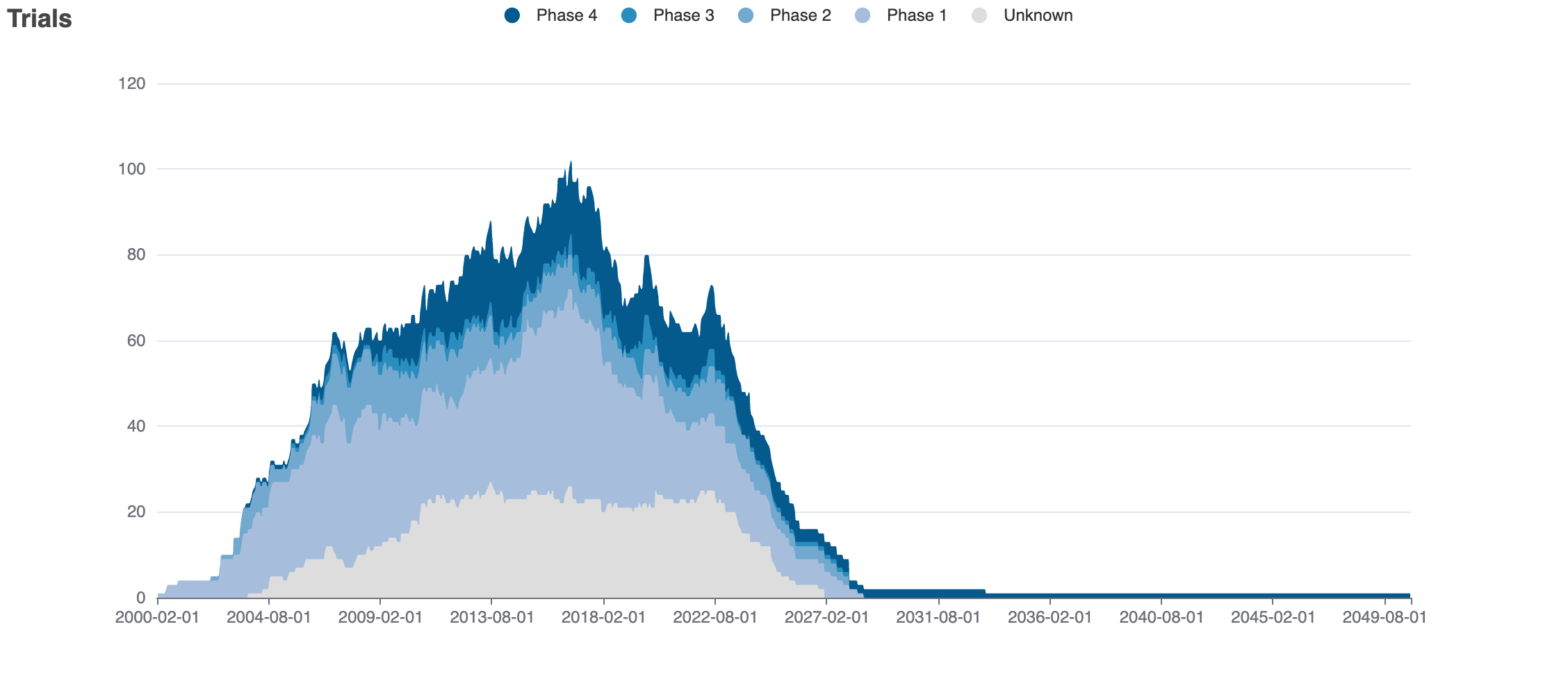
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Indications Phases 4
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver failure | D017093 | — | K72.9 | 1 | 2 | — | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Hepatitis | D006505 | — | K75.9 | — | 3 | 2 | 2 | — | 6 |
| Alcoholic liver diseases | D008108 | EFO_0008573 | K70 | — | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Hepatitis a | D006506 | EFO_0007305 | B15 | — | 2 | 1 | 2 | — | 4 |
| Hepatitis b | D006509 | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Major depressive disorder | D003865 | EFO_0003761 | F22 | 1 | 1 | — | 1 | — | 3 |
| End stage liver disease | D058625 | EFO_1001311 | K72.1 | 1 | 2 | — | 1 | — | 3 |
| Fibrosis | D005355 | — | — | — | 1 | — | 2 | — | 3 |
| Cholestasis | D002779 | — | K83.1 | — | — | 1 | 2 | — | 3 |
| Chronic hepatitis b | D019694 | EFO_0004239 | B18.1 | — | — | — | 1 | 1 | 2 |
Show 8 more
Indications Phases 3
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver diseases | D008107 | EFO_0001421 | K70-K77 | — | 1 | 3 | — | 2 | 6 |
| Depressive disorder | D003866 | EFO_1002014 | F32.A | 1 | 3 | 1 | — | 2 | 6 |
| Depression | D003863 | — | F33.9 | — | 3 | 1 | — | 3 | 6 |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | D065626 | EFO_0003095 | K75.81 | — | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Fatty liver | D005234 | EFO_0003934 | — | — | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Hepatitis c | D006526 | — | B19.2 | — | 3 | 1 | — | — | 3 |
| Chronic hepatitis c | D019698 | EFO_0004220 | B18.2 | — | 2 | 1 | — | — | 2 |
| Arthritis | D001168 | EFO_0005856 | M05-M14 | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | 2 |
| Juvenile arthritis | D001171 | EFO_1002007 | M08 | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
| Prostatic neoplasms | D011471 | — | C61 | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
Show 3 more
Indications Phases 2
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical and drug induced liver injury | D056486 | EFO_0004228 | — | 2 | 3 | — | — | 1 | 4 |
| Cognitive dysfunction | D060825 | — | G31.84 | — | 2 | — | — | 1 | 3 |
| Hepatic insufficiency | D048550 | — | — | 1 | 2 | — | — | 1 | 3 |
| Liver neoplasms | D008113 | EFO_1001513 | C22.0 | 1 | 1 | — | — | 1 | 3 |
| Chronic chemical and drug induced liver injury | D056487 | EFO_1000905 | — | 2 | 2 | — | — | — | 2 |
| Disease | D004194 | EFO_0000408 | R69 | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | 2 |
| Acute-on-chronic liver failure | D065290 | — | — | 1 | 2 | — | — | — | 2 |
| Chronic hepatitis | D006521 | — | K73.9 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Memory disorders | D008569 | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Alzheimer disease | D000544 | EFO_0000249 | F03 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
Show 11 more
Indications Phases 1
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | D006528 | — | C22.0 | 1 | — | — | — | 2 | 3 |
| Hyperhomocysteinemia | D020138 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | 2 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | D002318 | EFO_0000319 | I98 | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | 2 |
| Recurrence | D012008 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | 2 |
| Carcinoma | D002277 | — | C80.0 | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | 2 |
Indications Without Phase
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malnutrition | D044342 | EFO_0008572 | E40-E46 | — | — | — | — | 4 | 4 |
| Severe acute malnutrition | D000067011 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 3 | 3 |
| Alcoholic fatty liver | D005235 | — | K70.0 | — | — | — | — | 2 | 2 |
| Metabolic syndrome | D024821 | EFO_0000195 | E88.810 | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Bipolar disorder | D001714 | EFO_0000289 | F30.9 | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation | D045164 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Breast neoplasms | D001943 | EFO_0003869 | C50 | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Anesthesia | D000758 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Tuberculosis | D014376 | EFO_0000774 | A15-A19 | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
| Pelvic organ prolapse | D056887 | EFO_0004710 | — | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 |
Show 15 more
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | Ademetionine |
| INN | ademetionine |
| Description | S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952.
|
| Classification | Small molecule |
| Drug class | — |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)[O-])C[C@H]1O[C@@H](n2cnc3c(N)ncnc32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | 29908-03-0 |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1088977 |
| ChEBI ID | 67040 |
| PubChem CID | 9865604 |
| DrugBank | — |
| UNII ID | 7LP2MPO46S (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
No data
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
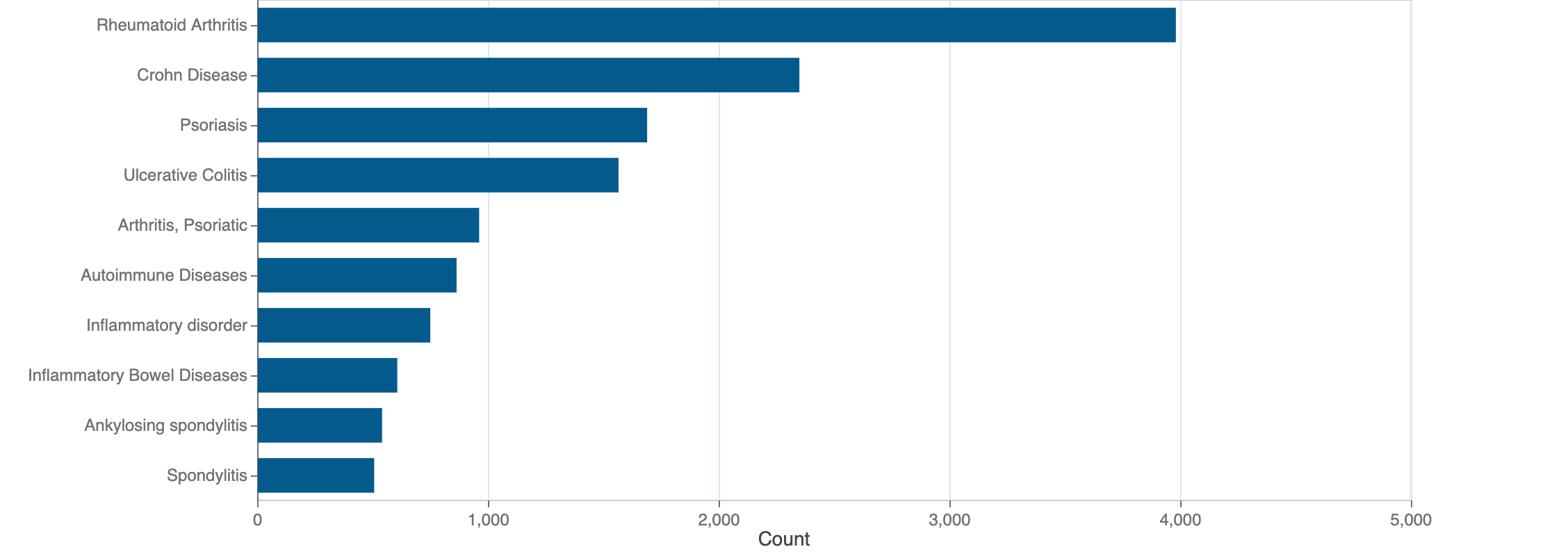
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 9,999 documents
View more details
Safety
Black-box Warning
No Black-box warning
Adverse Events
Top Adverse Reactions
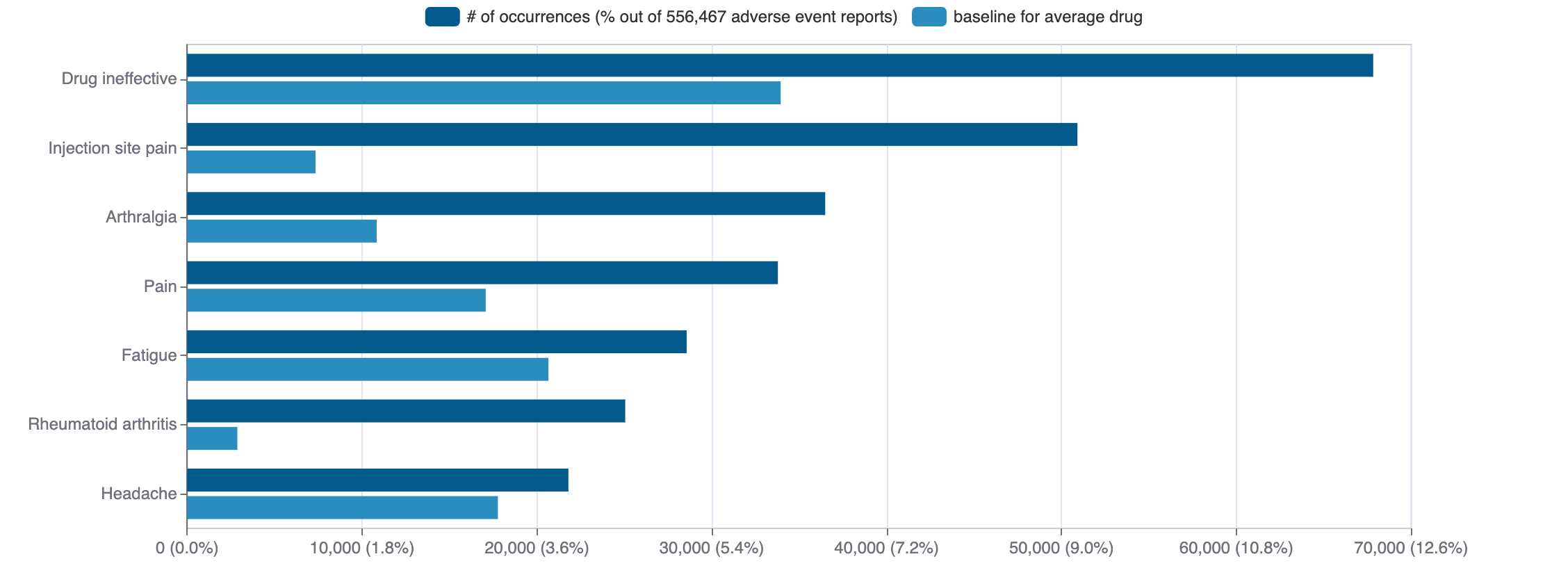
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
153 adverse events reported
View more details
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use