Zotiraciclib
Zotiraciclib is a small molecule pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies. It is known to target receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3, cyclin-dependent kinase 1, cyclin-dependent kinase 3, macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor, cyclin-dependent kinase 2, cyclin-dependent kinase 9, tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2, cyclin-dependent kinase 5, non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2, and tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
No data
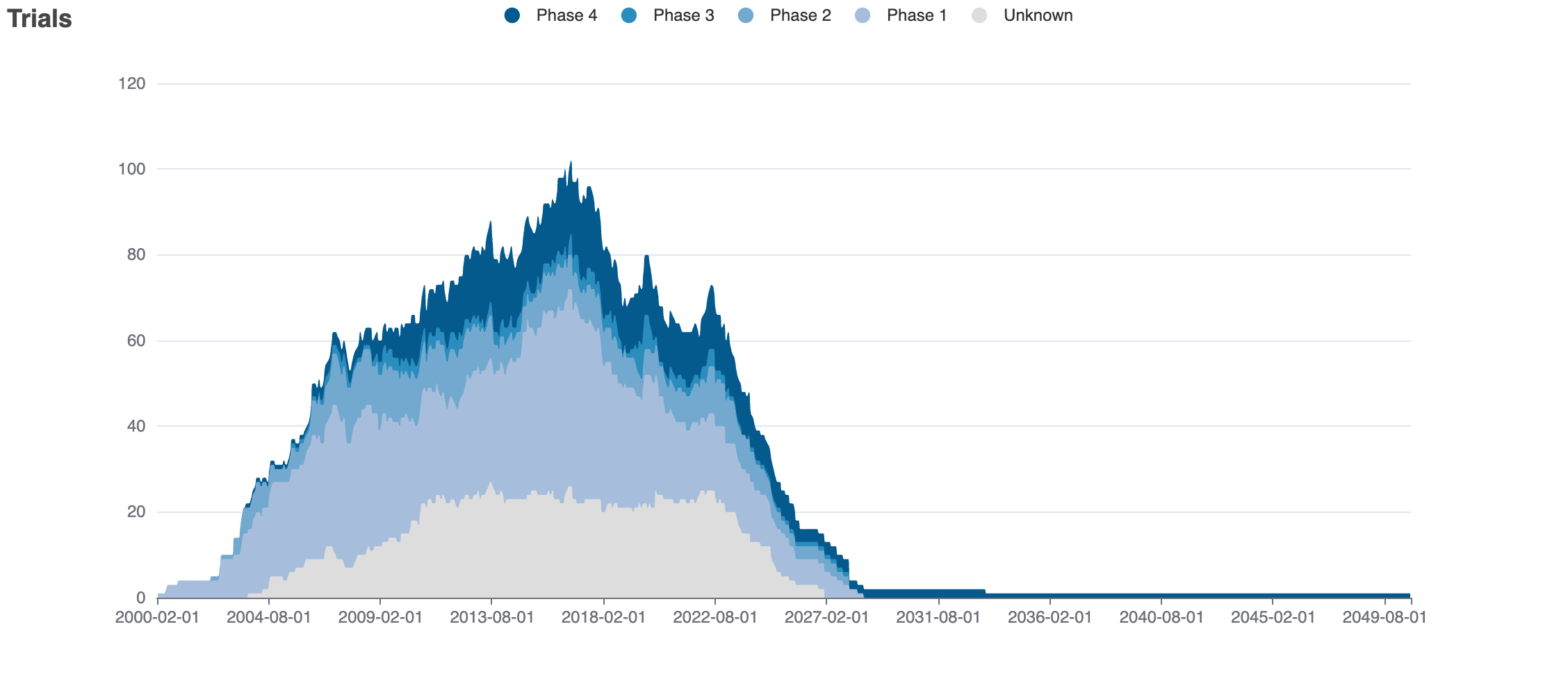
Clinical
Clinical Trials
46 clinical trials
View more details
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Indications Phases 4
No data
Indications Phases 3
No data
Indications Phases 2
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple sclerosis | D009103 | EFO_0003885 | G35 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Disease progression | D018450 | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Neoplasm metastasis | D009362 | EFO_0009708 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Autoimmune diseases | D001327 | EFO_0000540 | M30-M36 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Nervous system diseases | D009422 | — | G00-G99 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Autoimmune diseases of the nervous system | D020274 | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Chronic progressive multiple sclerosis | D020528 | EFO_0003840 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Sclerosis | D012598 | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Phases 1
No data
Indications Without Phase
No data
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | Zotiraciclib |
| INN | zotiraciclib |
| Description | Zotiraciclib (TG02) is a potent oral spectrum selective[clarification needed] kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. It was discovered in Singapore by S*BIO Pte Ltd and falls under the category of small molecule macrocycles. It crosses the blood brain barrier and acts by depleting Myc through the inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9). It is one of a number of CDK inhibitors under investigation; others targeting CDK9 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia include alvocidib and atuveciclib.
Myc overexpression is a known factor in many cancers, with 80 percent of glioblastomas characterized by this property. Zotiraciclib has been granted orphan drug designation by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of gliomas.
|
| Classification | Small molecule |
| Drug class | cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (formerly-cidib) |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | CN1C/C=C/CCOc2cccc(c2)-c2ccnc(n2)Nc2cccc(c2)C1 |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | 1204918-72-8 |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1944698 |
| ChEBI ID | — |
| PubChem CID | 16739650 |
| DrugBank | — |
| UNII ID | 40D08182TT (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
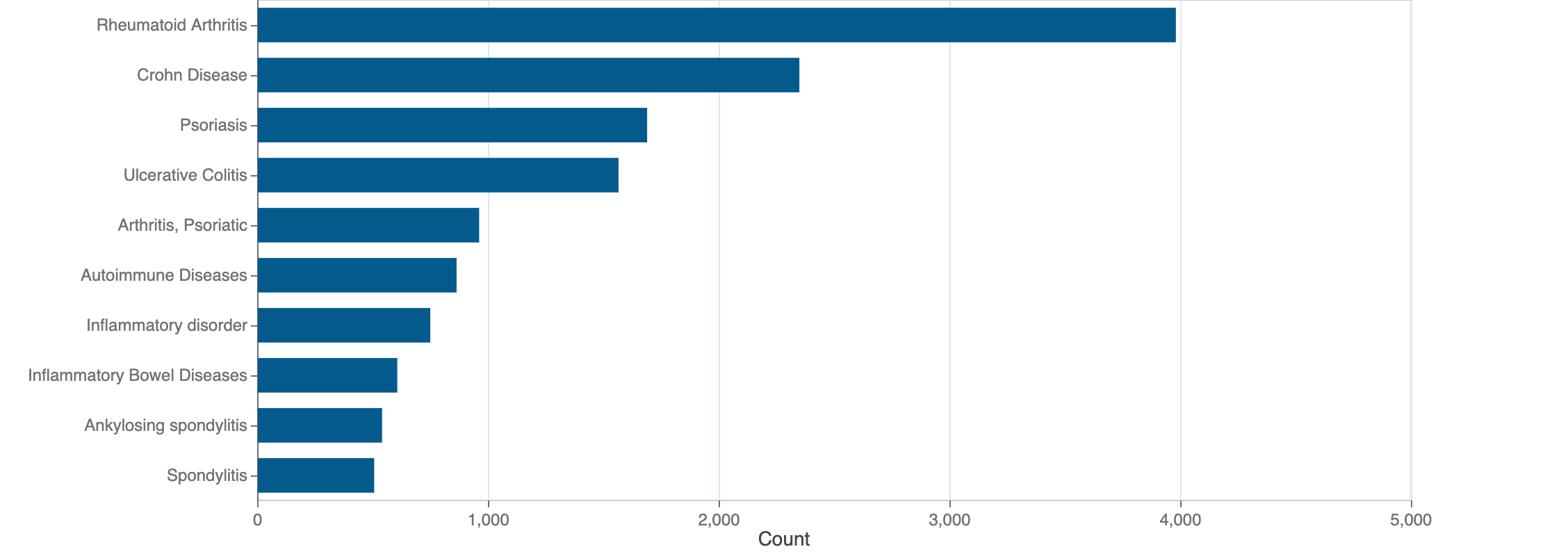
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 569 documents
View more details
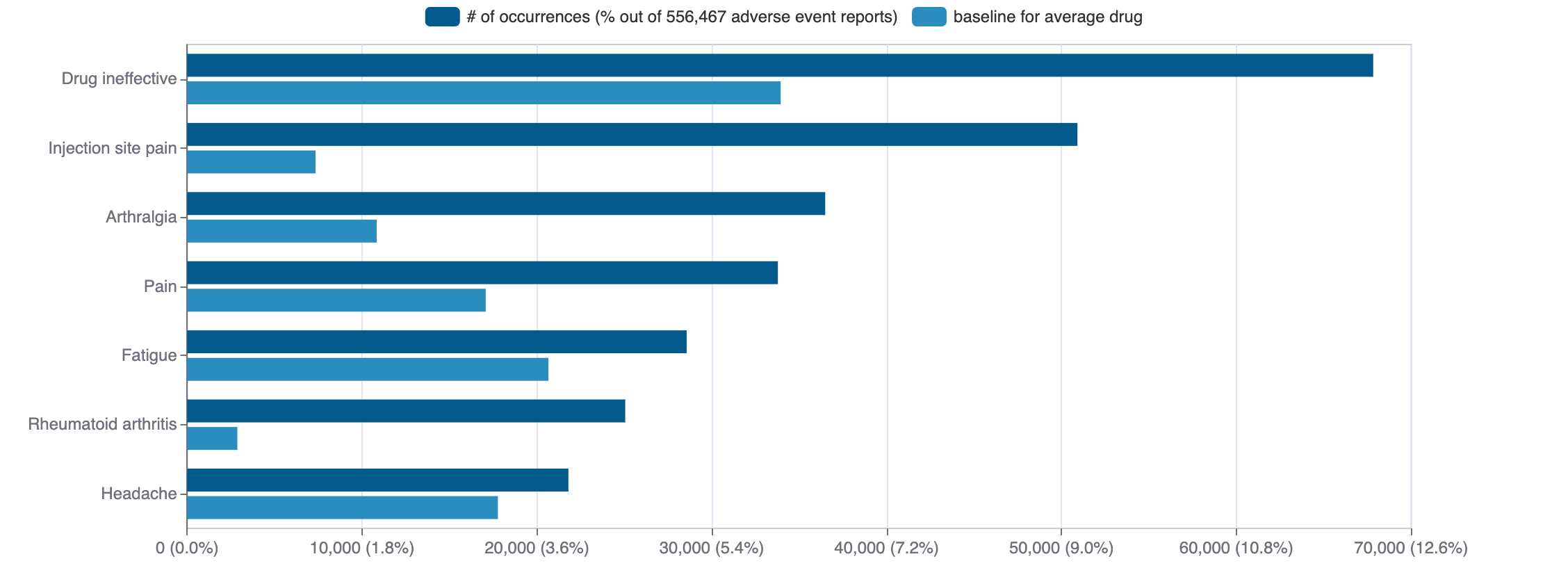
Safety
Black-box Warning
No Black-box warning
Adverse Events
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use