Rifalazil
Rifalazil is a small molecule pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
No data
Clinical
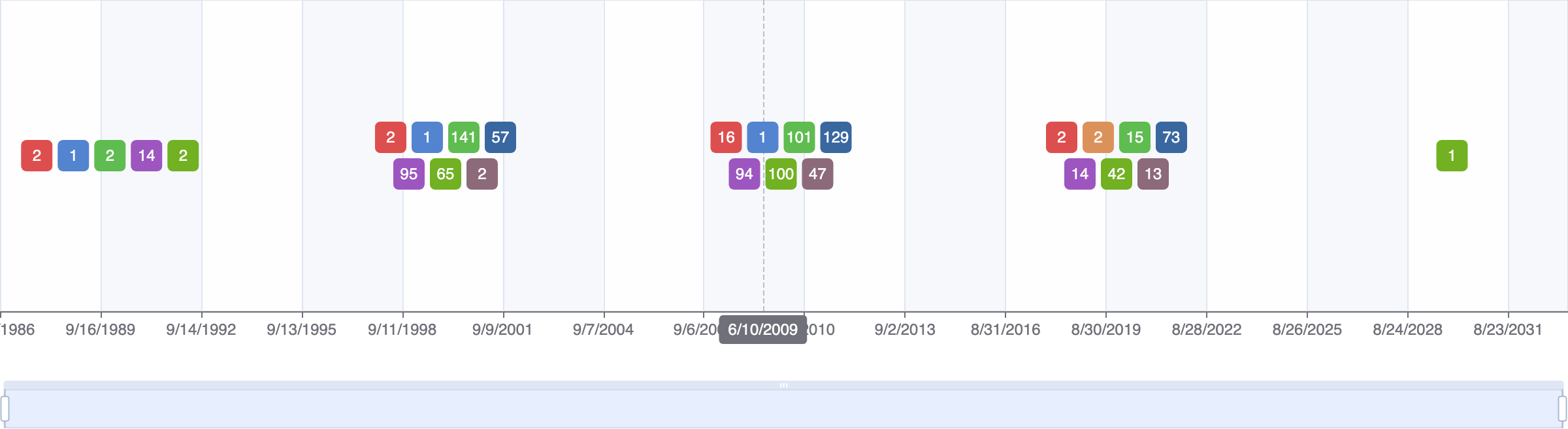
Clinical Trials
3 clinical trials
View more details
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
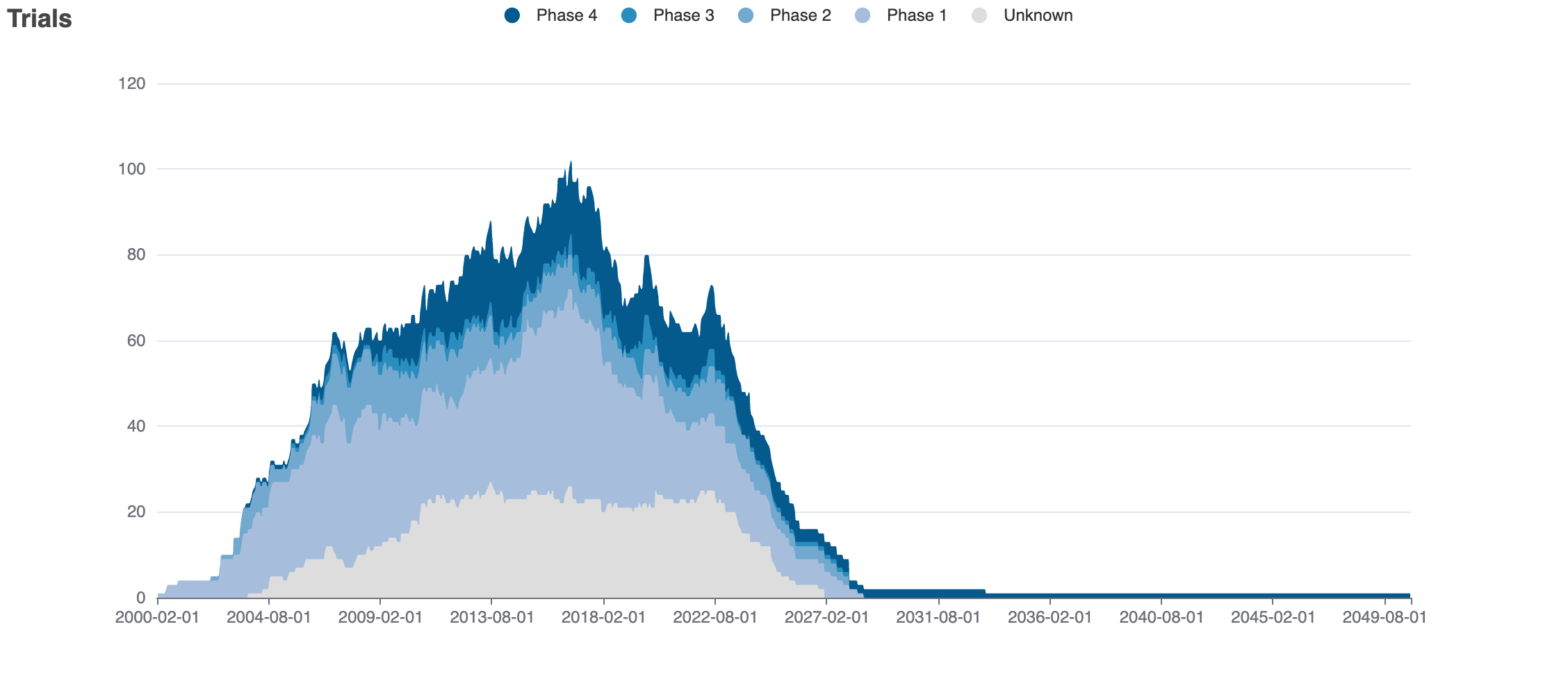
Indications Phases 4
No data
Indications Phases 3
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascular diseases | D014652 | EFO_0004264 | I77 | — | 1 | 1 | — | — | 2 |
| Peripheral arterial disease | D058729 | EFO_0004265 | — | — | 1 | 1 | — | — | 2 |
| Peripheral vascular diseases | D016491 | EFO_0003875 | I73.9 | — | 1 | 1 | — | — | 2 |
| Intermittent claudication | D007383 | EFO_0003876 | I73.9 | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
Indications Phases 2
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infections | D007239 | EFO_0000544 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Communicable diseases | D003141 | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Chlamydia infections | D002690 | EFO_0007205 | A74.9 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Cerebrovascular disorders | D002561 | EFO_0003763 | I60-I69 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Coronary artery disease | D003324 | — | I25.1 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Phases 1
No data
Indications Without Phase
No data
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | Rifalazil |
| INN | rifalazil |
| Description | Rifalazil (also known as KRM-1648 and AMI-1648) is an antibiotic substance that kills bacterial cells by blocking off the β-subunit in RNA polymerase. Rifalazil is used as a treatment for many different diseases. The most common are Chlamydia infection, Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD), and tuberculosis (TB). Using rifalazil and the effects that coincide with taking rifalazil for treating a bacterial disease vary from person to person, as does any drug put into the human body. Food interactions and genetic variation are a few causes for the variation in side effects from the use of rifalazil. Its development was terminated in 2013 due to severe side effects.
|
| Classification | Small molecule |
| Drug class | antibiotics (rifamycin derivatives) |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | CO[C@H]1/C=C/O[C@@]2(C)Oc3c(C)c(O)c4c(=O)c(c5oc6cc(N7CCN(CC(C)C)CC7)cc(O)c6nc-5c4c3C2=O)NC(=O)/C(C)=C\C=C\[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)[C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@H]1C |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | — |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL236297 |
| ChEBI ID | — |
| PubChem CID | 6540558 |
| DrugBank | — |
| UNII ID | S1976TE8QK (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
No data
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
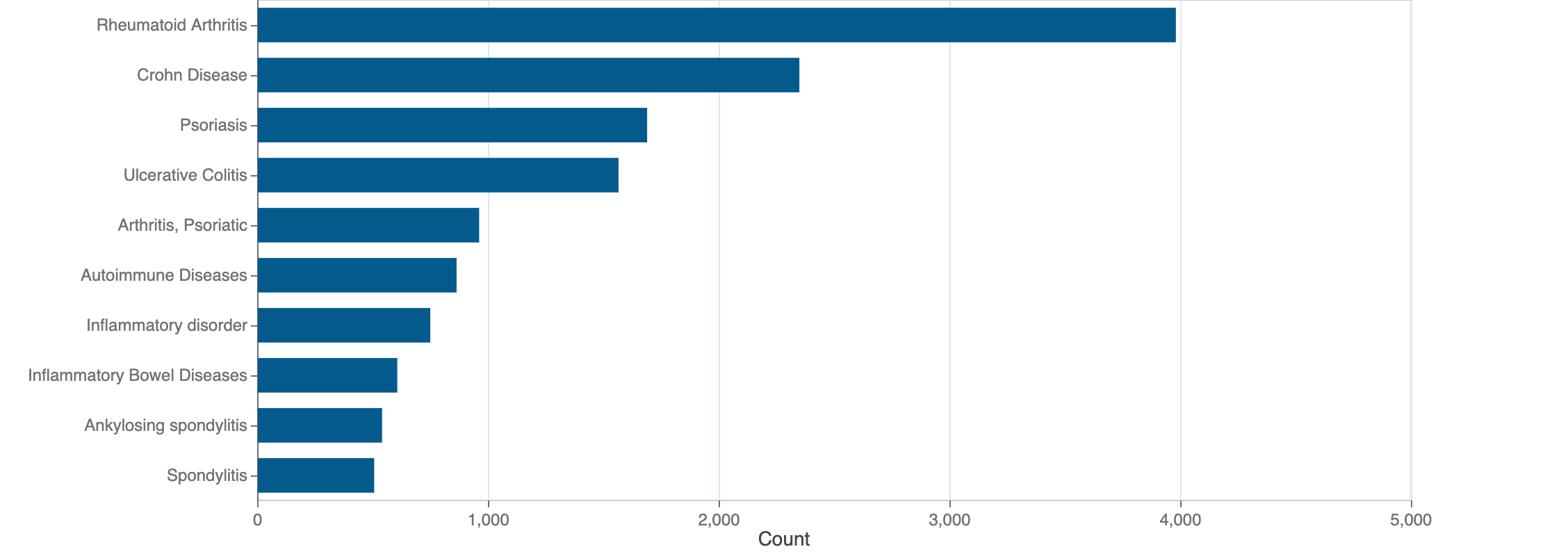
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 200 documents
View more details
Safety
Black-box Warning
No Black-box warning
Adverse Events
0 adverse events reported
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use