GALIDESIVIR
Galidesivir is a small molecule pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
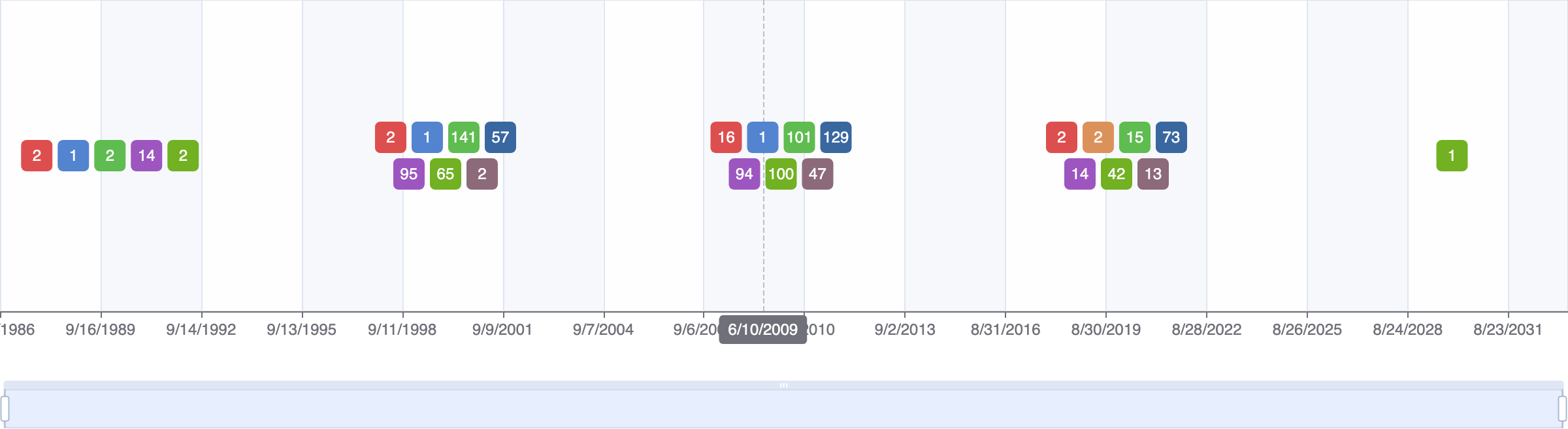
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
No data
Clinical
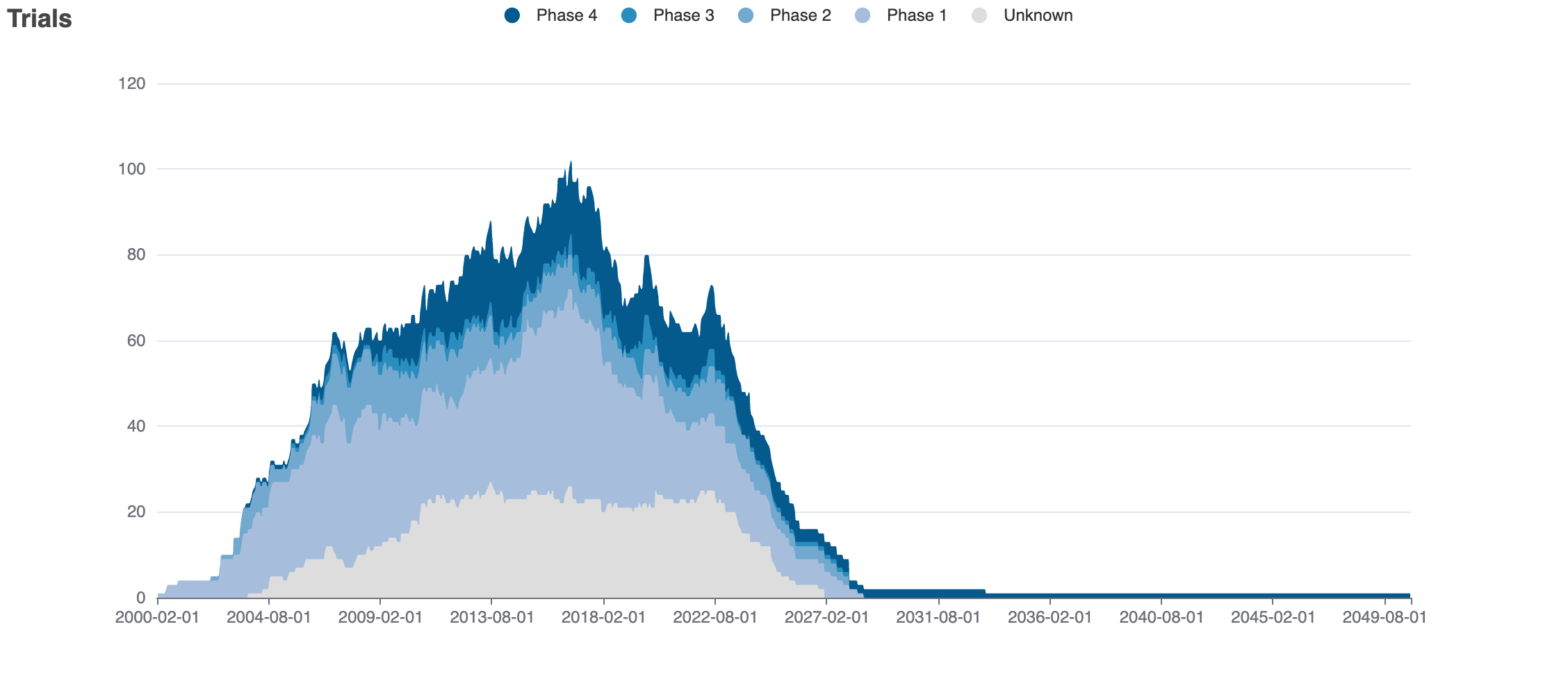
Clinical Trials
4 clinical trials
View more details
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Indications Phases 4
No data
Indications Phases 3
No data
Indications Phases 2
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | D016773 | — | B55.1 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Leishmaniasis | D007896 | EFO_0005044 | B55 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Phases 1
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covid-19 | D000086382 | — | U07.1 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Fever | D005334 | — | R50.9 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Yellow fever | D015004 | — | A95 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Virus diseases | D014777 | — | B34 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Marburg virus disease | D008379 | EFO_0007358 | A98.3 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Ebola hemorrhagic fever | D019142 | EFO_0007243 | A98.4 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Infections | D007239 | EFO_0000544 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Communicable diseases | D003141 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Filoviridae infections | D018702 | EFO_0007273 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Without Phase
No data
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | GALIDESIVIR |
| INN | galidesivir |
| Description | Galidesivir (BCX4430, immucillin-A) is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog (a type of nucleoside analog). It was developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals with funding from NIAID, originally intended as a treatment for hepatitis C, but subsequently developed as a potential treatment for deadly filovirus infections such as Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus disease, as well as Zika virus. Currently, galidesivir is under phase 1 human trial in Brazil for coronavirus.
|
| Classification | Small molecule |
| Drug class | antivirals: adenosine analogs acting as RNA polymerase inhibitors |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | Nc1ncnc2c([C@@H]3N[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]3O)c[nH]c12 |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | 222631-44-9 |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1236524 |
| ChEBI ID | — |
| PubChem CID | 69211190 |
| DrugBank | — |
| UNII ID | OLF97F86A7 (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
No data
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
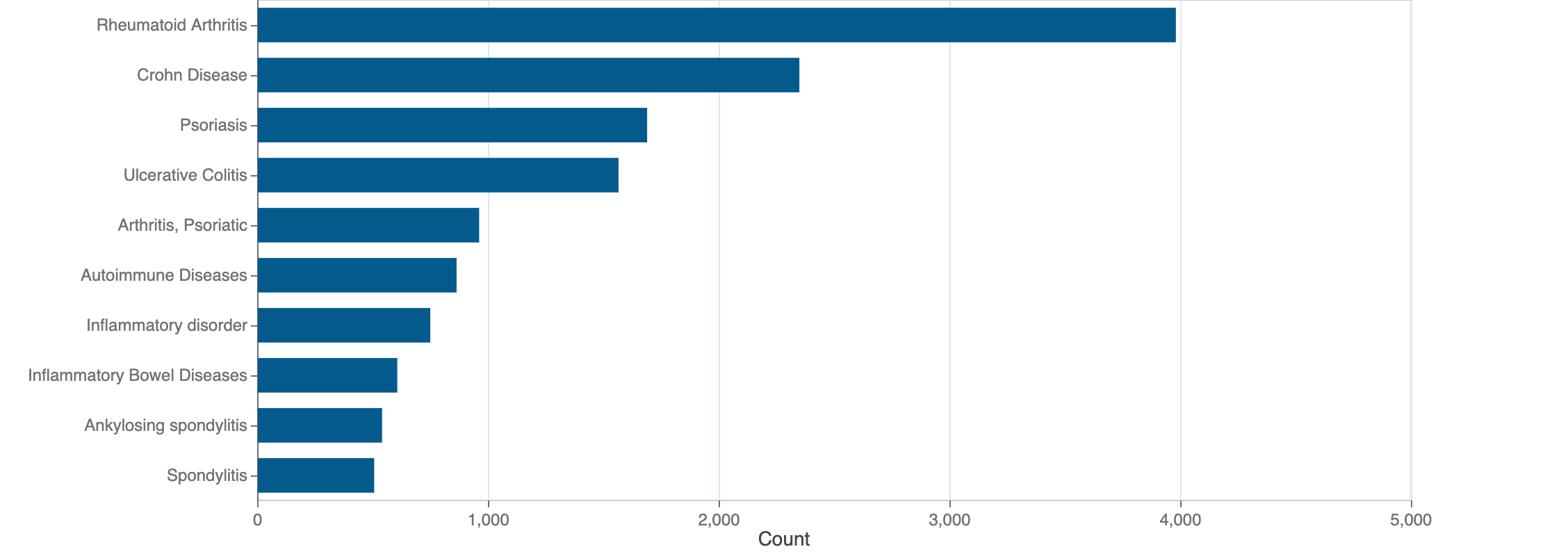
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 1,667 documents
View more details
Safety
Black-box Warning
No Black-box warning
Adverse Events
0 adverse events reported
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use