Cosfroviximab
Cosfroviximab is an antibody pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
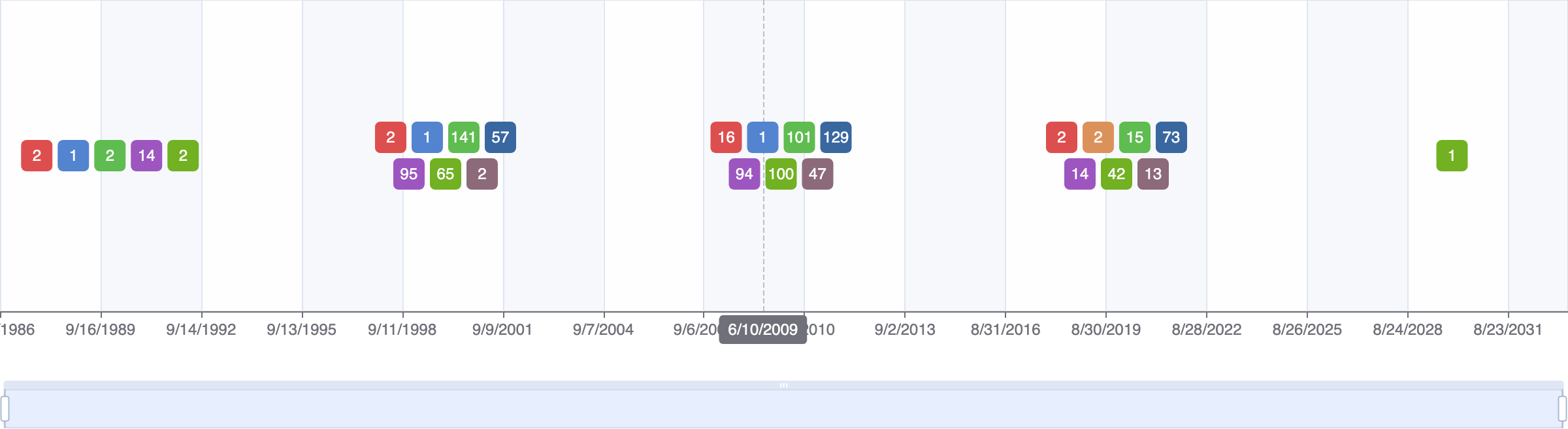
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
No data
Clinical
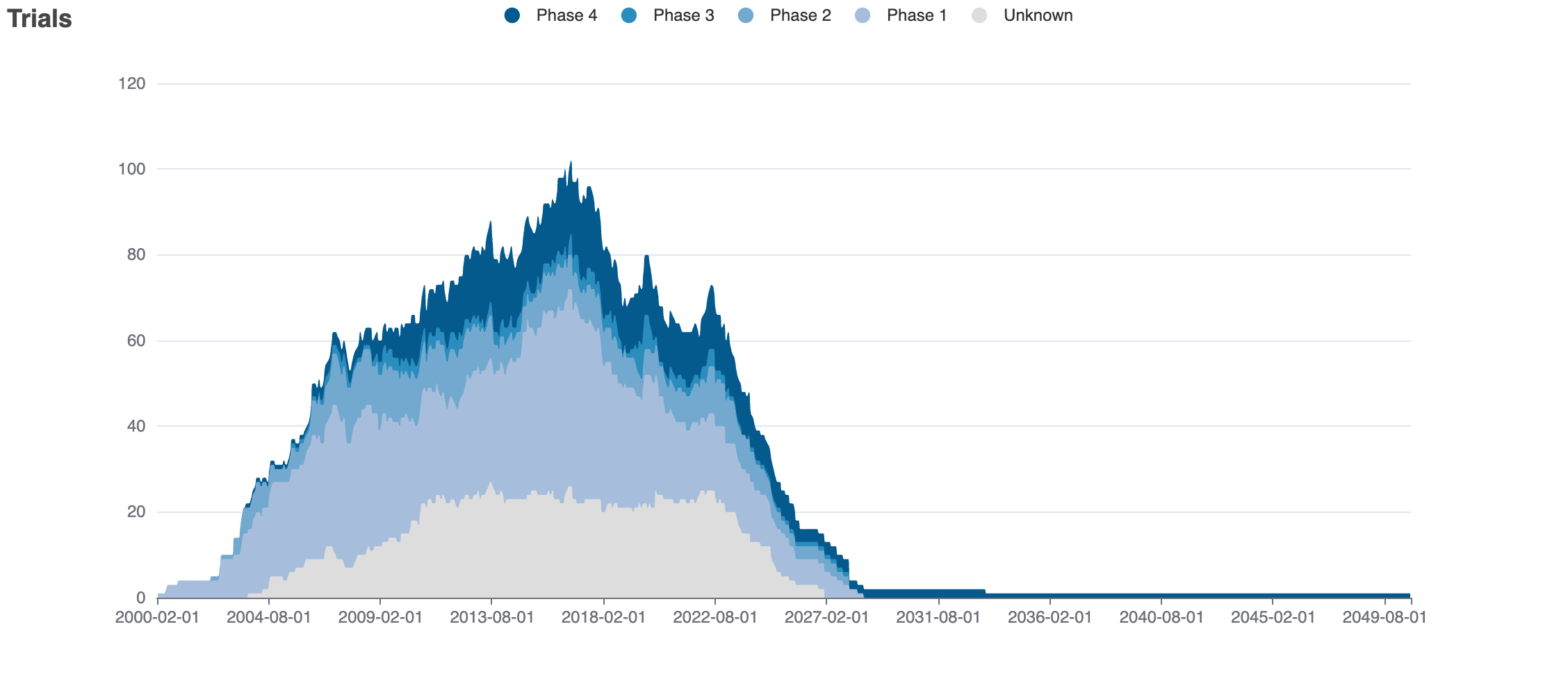
Clinical Trials
19 clinical trials
View more details
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Indications Phases 4
No data
Indications Phases 3
No data
Indications Phases 2
No data
Indications Phases 1
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy volunteers/patients | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Without Phase
No data
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | Cosfroviximab |
| INN | cosfroviximab |
| Description | ZMapp is an experimental biopharmaceutical drug comprising three chimeric monoclonal antibodies under development as a treatment for Ebola virus disease. Two of the three components were originally developed at the Public Health Agency of Canada's National Microbiology Laboratory (NML), and the third at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases; the cocktail was optimized by Gary Kobinger, a research scientist at the NML and underwent further development under license by Mapp Biopharmaceutical. ZMapp was first used on humans during the Western African Ebola virus epidemic, having only been previously tested on animals and not yet subjected to a randomized controlled trial. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) ran a clinical trial starting in January 2015 with subjects from Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Liberia aiming to enroll 200 people, but the epidemic waned and the trial closed early, leaving it too statistically underpowered to give a meaningful result about whether ZMapp worked.
|
| Classification | Antibody |
| Drug class | monoclonal antibodies |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | — |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | — |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL3990001 |
| ChEBI ID | — |
| PubChem CID | — |
| DrugBank | — |
| UNII ID | 820CI2BHRP (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
No data
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 9,999 documents
View more details
Safety
Black-box Warning
No Black-box warning
Adverse Events
0 adverse events reported
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use