Benserazide
Benserazide is a small molecule pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies. It is known to target cystathionine beta-synthase and aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
No data
Clinical
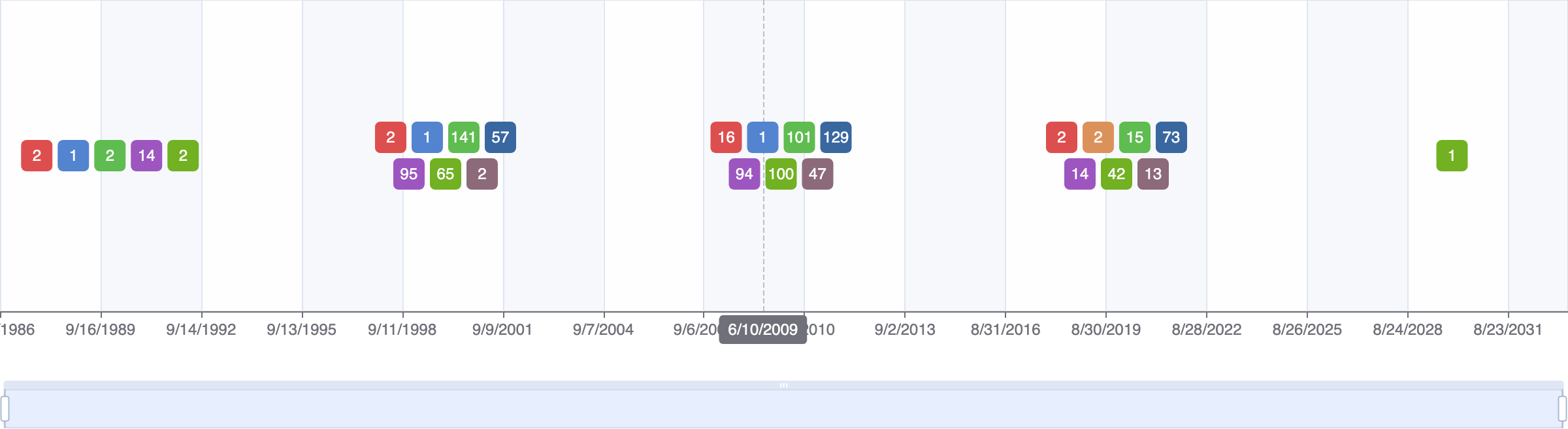
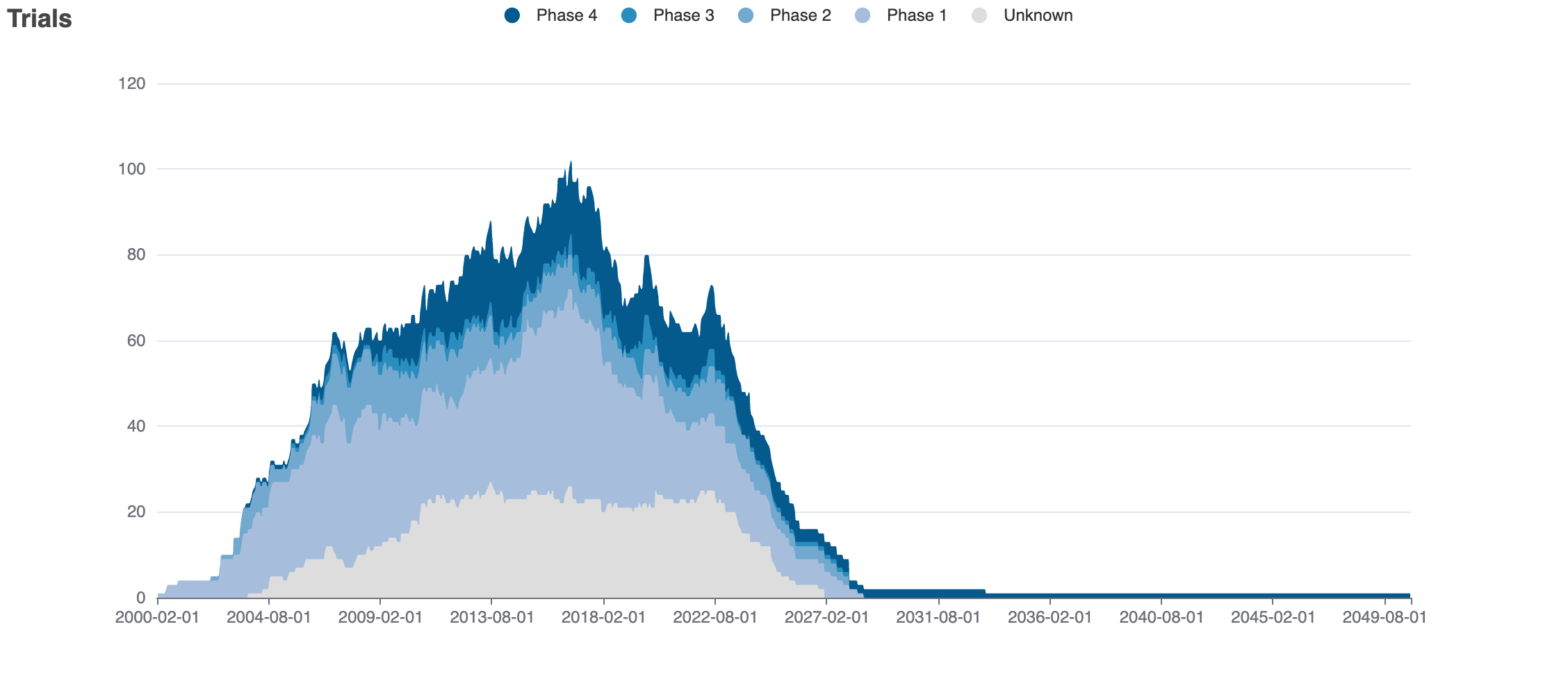
Clinical Trials
36 clinical trials
View more details
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Indications Phases 4
No data
Indications Phases 3
No data
Indications Phases 2
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson disease | D010300 | EFO_0002508 | G20 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Phases 1
No data
Indications Without Phase
No data
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | Benserazide |
| INN | benserazide |
| Description | Benserazide is a carbohydrazide that results from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of DL-serine with the primary amino group of 4-(hydrazinylmethyl)benzene-1,2,3-triol. An aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase inhibitor (DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor) that does not enter the central nervous system, it is used as its hydrochloride salt as an adjunct to levodopa in the treatment of parkinsonism. By preventing the conversion of levodopa to dopamine in the periphery, it causes an increase in the amount of levodopa reaching the central nervous system and so reduces the required dose. Benserazide has no antiparkinson actions when given alone. It has a role as an EC 4.1.1.28 (aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase) inhibitor, an antiparkinson drug and a dopaminergic agent. It is a carbohydrazide, a member of catechols, a primary amino compound and a primary alcohol. It is a conjugate base of a benserazide(1+). |
| Classification | Small molecule |
| Drug class | — |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | NC(CO)C(=O)NNCc1ccc(O)c(O)c1O |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | 322-35-0 |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1096979 |
| ChEBI ID | 64187 |
| PubChem CID | 2327 |
| DrugBank | DB12783 |
| UNII ID | 762OS3ZEJU (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
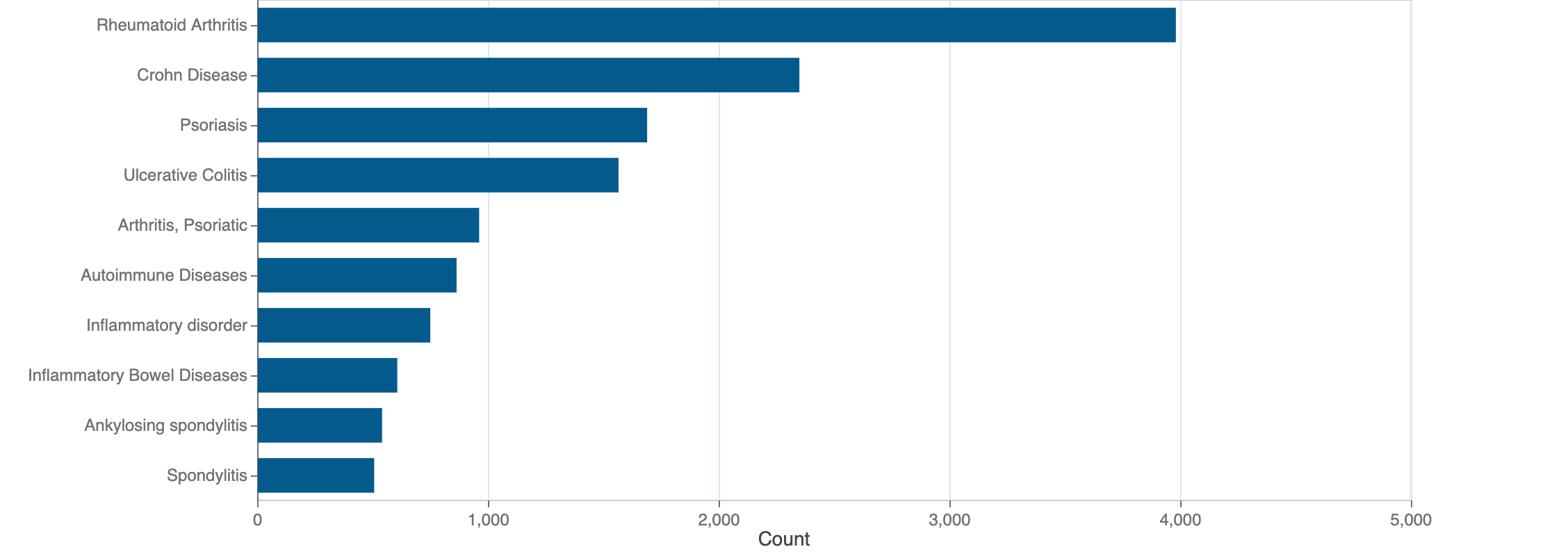
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 2,849 documents
View more details
Safety
Black-box Warning
No Black-box warning
Adverse Events
Top Adverse Reactions
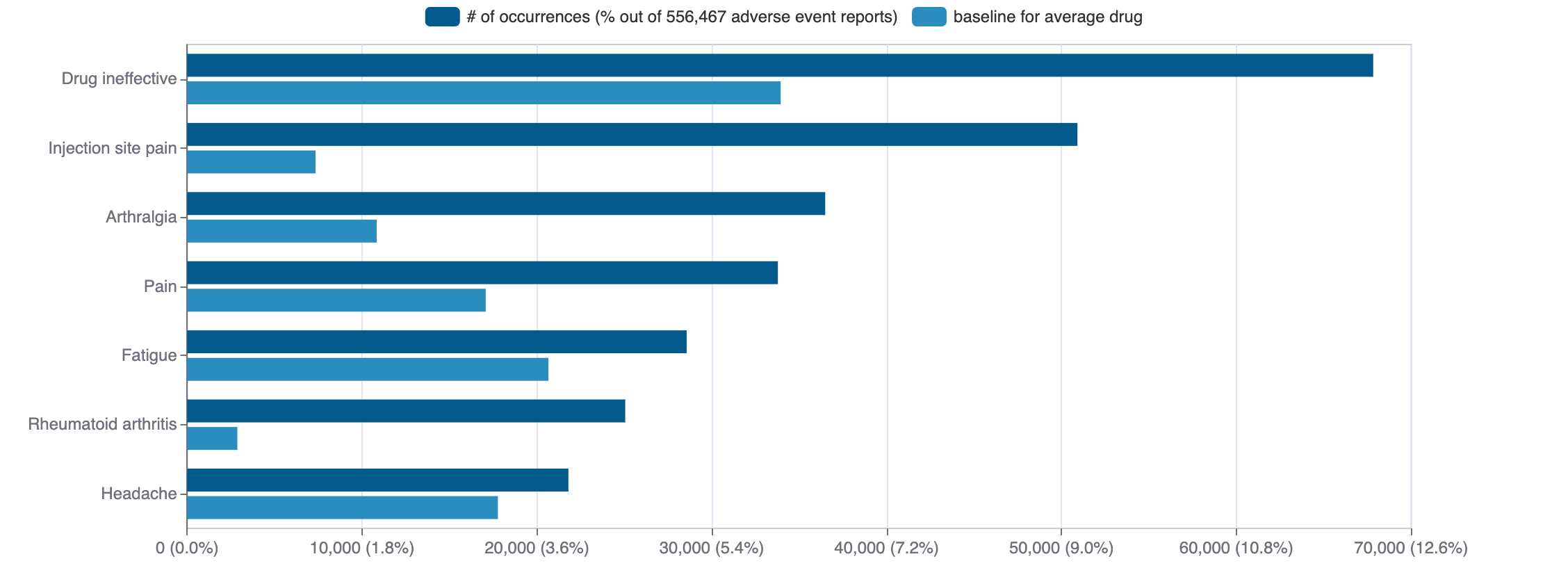
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
2,512 adverse events reported
View more details
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use