Polyglycolic acid
Polyglycolic acid is a small molecule pharmaceutical. It is currently being investigated in clinical studies.
Download report
Favorite
Events Timeline
Commercial
Clinical
Drug
Target
Variants
Financial
Trends
Safety
Events Timeline
5D
1M
3M
6M
YTD
1Y
2Y
5Y
Max
Events
FDA approval date
EMA approval date
Patent expiration date
Study first post date
Last update post date
Start date
Primary completion date
Completion date
Results first post date
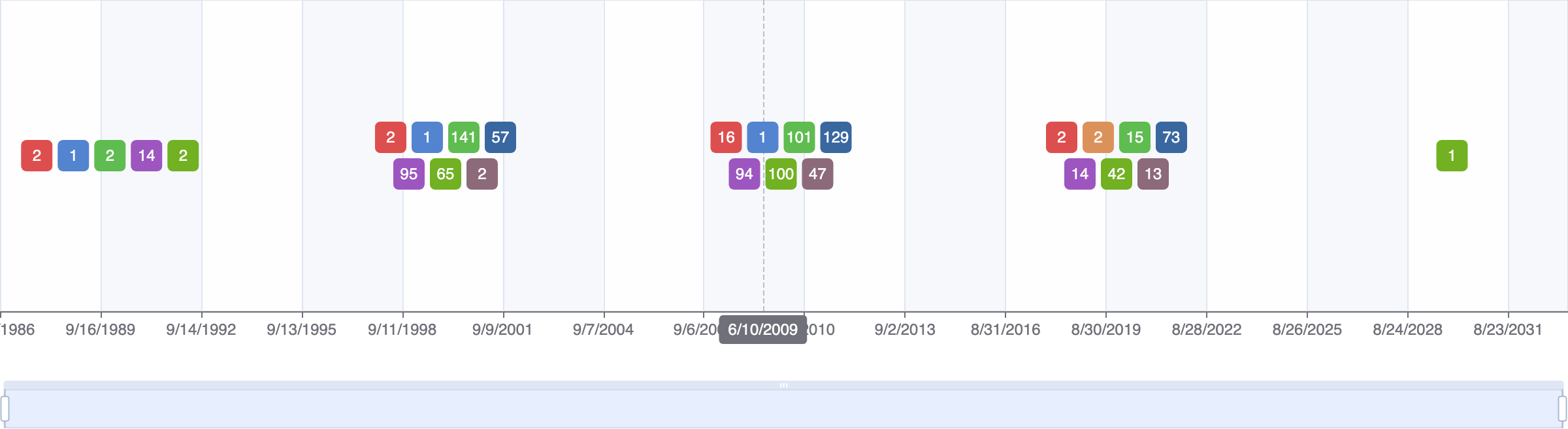
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Commercial
Therapeutic Areas
No data
Trade Name
FDA
EMA
No data
Drug Products
FDA
EMA
New Drug Application (NDA)
New Drug Application (NDA)
Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA)
Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA)
No data
Labels
FDA
EMA
Brand Name | Status | Last Update |
|---|---|---|
| perseris | New Drug Application | 2025-01-28 |
Indications
FDA
EMA
No data
Agency Specific
FDA
EMA
No data
Patent Expiration
No data
ATC Codes
No data
HCPCS
No data
Clinical
Clinical Trials
2502 clinical trials
View more details
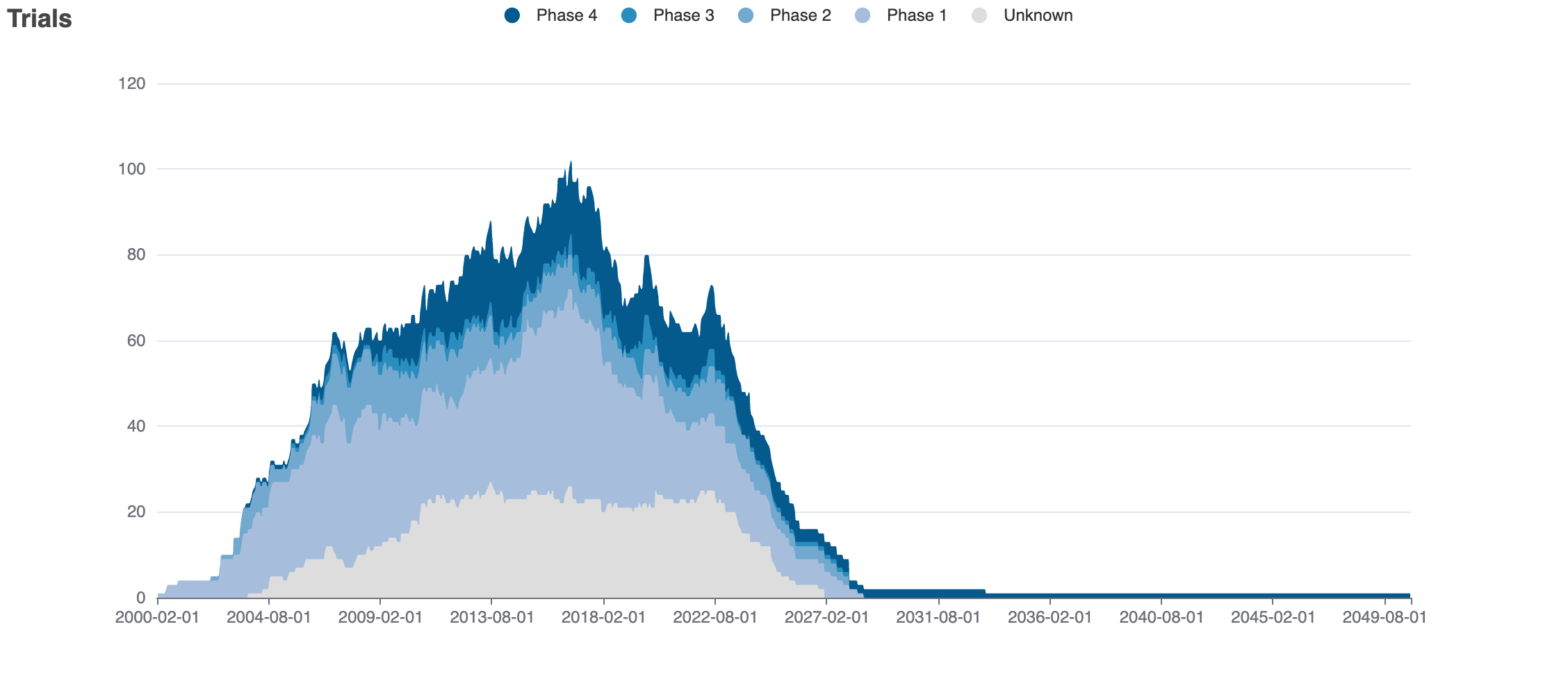
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Indications Phases 4
No data
Indications Phases 3
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal neoplasms | D015179 | — | — | 3 | 8 | 6 | — | — | 17 |
| Colonic neoplasms | D003110 | — | C18 | 2 | — | 1 | — | — | 3 |
| Rectal neoplasms | D012004 | — | — | 2 | — | 1 | — | — | 3 |
| Neoplasms | D009369 | — | C80 | — | — | 2 | — | — | 2 |
| Liver neoplasms | D008113 | EFO_1001513 | C22.0 | — | 1 | 1 | — | — | 2 |
| Gastrointestinal neoplasms | D005770 | — | C26.9 | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
| Digestive system neoplasms | D004067 | — | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
| Rectal diseases | D012002 | — | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | D005767 | — | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
| Intestinal neoplasms | D007414 | — | C26.0 | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 |
Show 3 more
Indications Phases 2
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esophageal neoplasms | D004938 | — | C15 | 1 | 1 | — | — | — | 2 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | D001172 | EFO_0000685 | M06.9 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Neoplasm metastasis | D009362 | EFO_0009708 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Diarrhea | D003967 | — | R19.7 | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | D008180 | EFO_0002690 | M32 | 1 | 1 | — | — | — | 1 |
Indications Phases 1
Indication | MeSH | Ontology | ICD-10 | Ph 1 | Ph 2 | Ph 3 | Ph 4 | Other | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | D002289 | — | — | 3 | — | — | — | — | 3 |
| Pancreatic ductal carcinoma | D021441 | — | — | 2 | — | — | — | — | 2 |
| Lung neoplasms | D008175 | — | C34.90 | 2 | — | — | — | — | 2 |
| Hiv infections | D015658 | EFO_0000764 | B20 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome | D000163 | EFO_0000765 | B20 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Toxoplasmosis | D014123 | EFO_0007517 | B58 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Cerebral toxoplasmosis | D016781 | EFO_0007200 | B58.2 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Encephalitis | D004660 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Stomach neoplasms | D013274 | EFO_0003897 | C16 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
| Thyroid neoplasms | D013964 | EFO_0003841 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 |
Show 2 more
Indications Without Phase
No data
Epidemiology
Epidemiological information for investigational and approved indications
View more details
Drug
General
| Drug common name | Polyglycolic acid |
| INN | polyglycolic acid |
| Description | Polyglycolide or poly(glycolic acid) (PGA), also spelled as polyglycolic acid, is a biodegradable, thermoplastic polymer and the simplest linear, aliphatic polyester. It can be prepared starting from glycolic acid by means of polycondensation or ring-opening polymerization. PGA has been known since 1954 as a tough fiber-forming polymer. Owing to its hydrolytic instability, however, its use has initially been limited. Currently polyglycolide and its copolymers (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) with lactic acid, poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) with ε-caprolactone and poly (glycolide-co-trimethylene carbonate) with trimethylene carbonate) are widely used as a material for the synthesis of absorbable sutures and are being evaluated in the biomedical field.
|
| Classification | Small molecule |
| Drug class | — |
| Image (chem structure or protein) |  |
| Structure (InChI/SMILES or Protein Sequence) | — |
Identifiers
| PDB | — |
| CAS-ID | 26009-03-0 |
| RxCUI | — |
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL2107965 |
| ChEBI ID | — |
| PubChem CID | — |
| DrugBank | — |
| UNII ID | H1IL6F7KB8 (ChemIDplus, GSRS) |
Target
No data
Variants
No data
Financial
No data
Trends
PubMed Central
Top Terms for Disease or Syndrome:
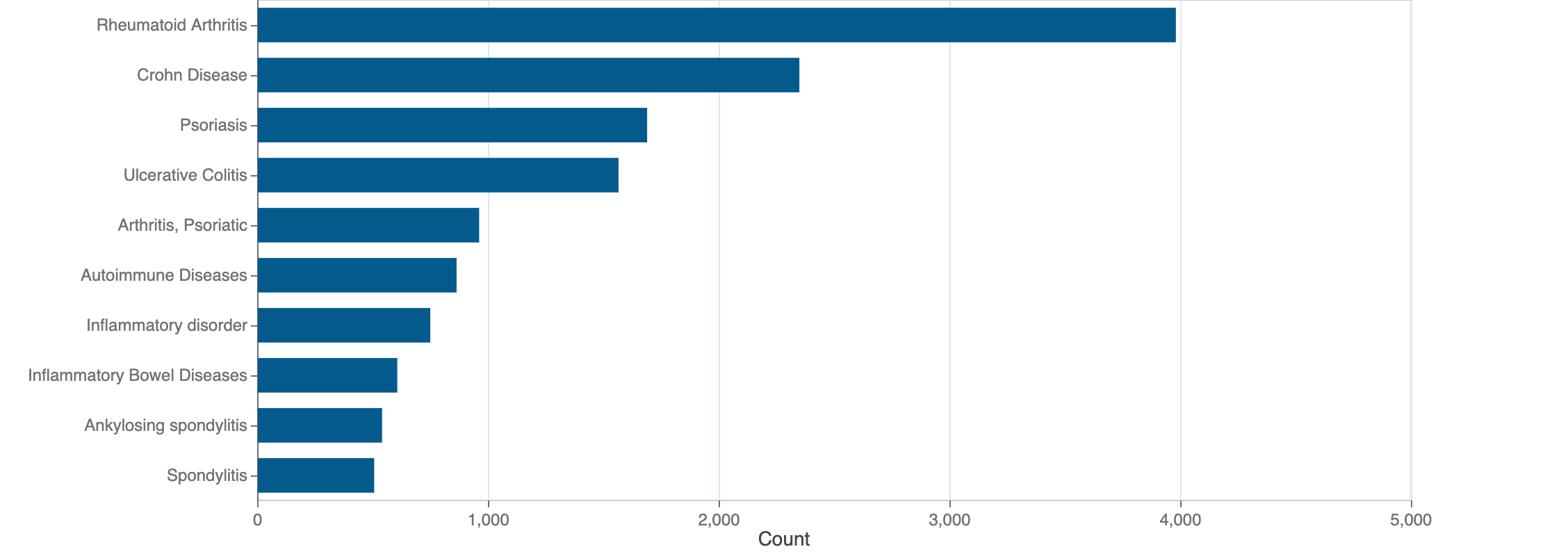
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
Additional graphs summarizing 36,187 documents
View more details
Safety
Black-box Warning
Black-box warning for: Perseris
Adverse Events
Top Adverse Reactions
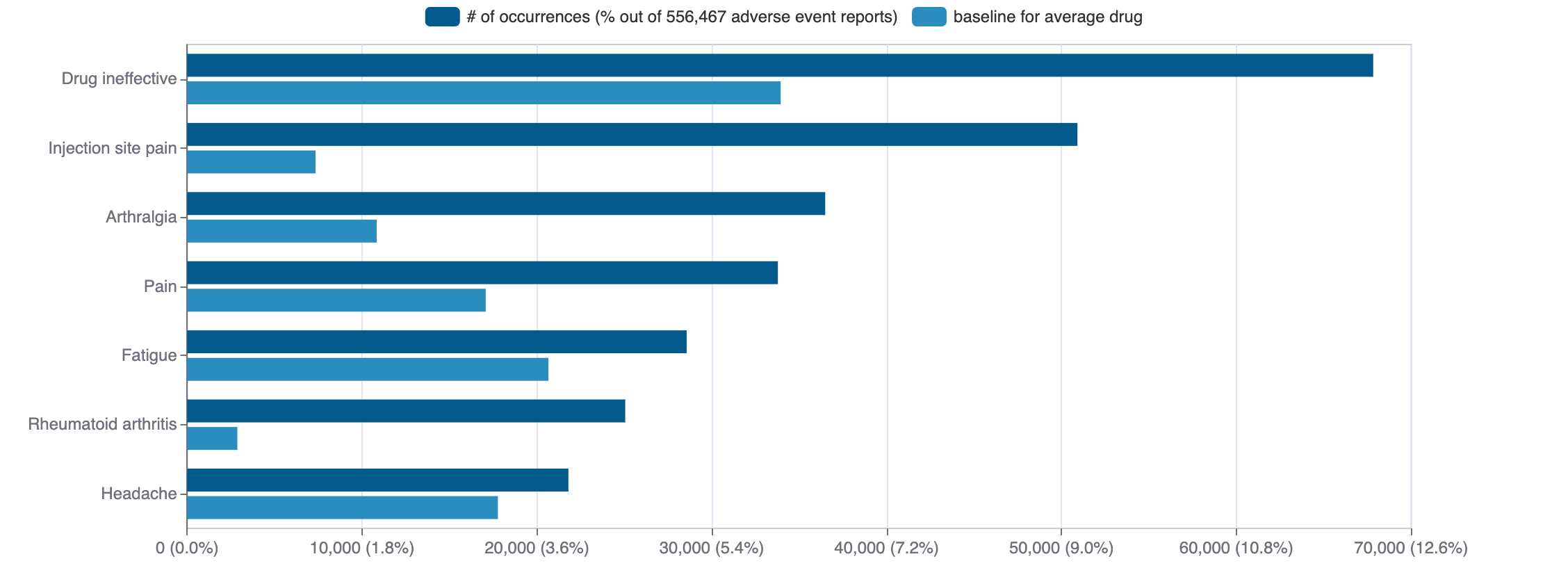
Mock data
Subscribe for the real data
Subscribe for the real data
51 adverse events reported
View more details
© 2020-2025 Collaborative Drug Discovery Inc. (CDD) | Terms of Use